Basics
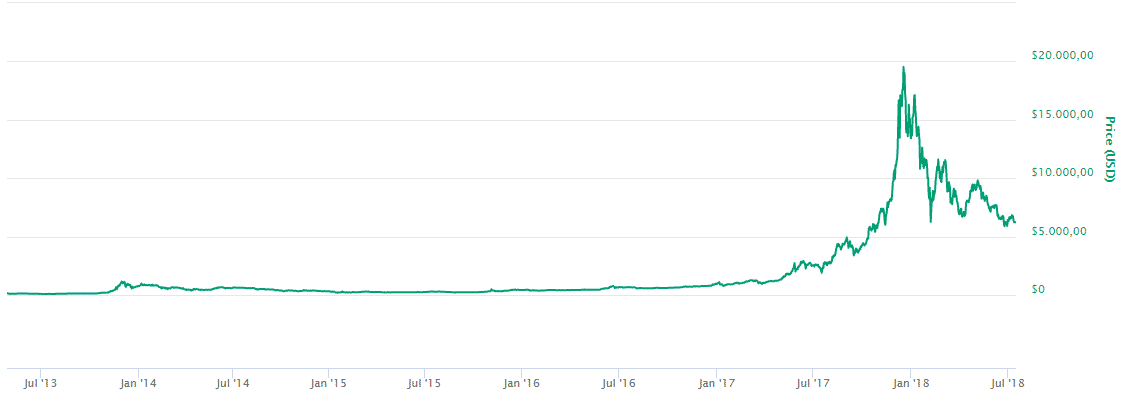
Cryptocurrencies and blockchains have been important topics since Bitcoin’s launch in 2009. The first real-world Bitcoin transaction was made in 2009 to buy two pizzas for 10,000 Bitcoins, now worth more than 62 million US Dollars. In December 2017, Bitcoin’s price peaked at $19,783 per Bitcoin. However, not only the value of Bitcoin increased significantly. Ethereum and many other cryptocurrencies took the original concept of a blockchain and extended it with features like smart contracts and decentralized apps. But why are cryptocurrencies so revolutionary? Also, what is a blockchain, and how does it work?
Why are cryptocurrencies so revolutionary?
The functions of money
There are three functions or services that money has to provide. Money has to serve as a medium of exchange, as a store of value, and as a unit of account.
The first and most important function or service is the medium of exchange. Without money, transactions would have to be conducted by the exchange of goods. But to buy a good or service from somebody, you must own a good or service of equal value. This is a major problem solved with money as a medium of exchange, which all parties accept.
The second function is a store of value. Money must hold its value over time to be a medium of exchange. As a store of value, money is not unique. There are several other stores of value, such as property, stocks, and so on. However, money is more liquid than most other stores of value as it is a medium of exchange that is accepted everywhere.
The third and final function is the unit of account. Money is accepted as a medium of exchange, and it measures goods and services being exchanged.
From barter to bitcoin
Historically, there were several forms of money, such as gold, commodity money, or fiat money, which is the form of money we use today. Even though gold is a good store of value, it is very hard to transport because of its weight, and it’s even more difficult to split an ounce of gold into two pieces. Commodity money is paper money that is linked to an amount of gold. This makes it easier to transport and better to split than gold.
So why do we use fiat money today when commodity money is already a great medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account? In 1973, the link between gold and money was removed. Banks weren’t allowed to exchange gold ounces for commodity money anymore. This new form of money is called fiat money. Central banks worldwide can print fiat money, not linked to gold or other goods. So, fiat money relies solely on our trust in central banks.
Why use cryptocurrencies?
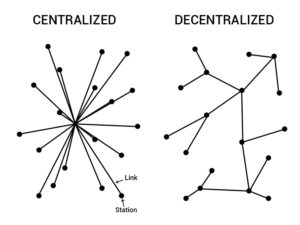
Unlike fiat money, cryptocurrencies don’t rely on central institutions like banks and aren’t controlled by them. They are decentralized. Decentralized systems are accessible from everywhere, at any time, and everybody can join. They have strict rules that everybody has to follow. Furthermore, decentralized systems are hard to hack because no single institution holds the money. The most well-known form of a decentralized system is the blockchain.
Cryptocurrencies also have a limited supply. Central banks can print as much money as needed to manipulate a currency’s value. This isn’t possible with cryptocurrencies because no central institution can manipulate the supply. Because of the limited supply, cryptocurrencies are more attractive as an asset.
Transactions on blockchains cannot be forced or reversed. Banks have control over your accounts and transactions. They can deduct money from your account without your permission, and they can reverse transactions. Transactions on the blockchain can’t be reversed.
A blockchain is a chain of blocks that contains information. Every block on the chain contains a number of accepted transactions and a hash of the previous block. When enough transactions are added to the block, the block will be added to the blockchain and then distributed to the network of communicating nodes running the software. The nodes must save the whole blockchain and check every block against consensus rules. Some nodes are mining nodes. They add blocks to the blockchain by solving a mathematical puzzle and including the answer in the block. Miners receive rewards in the form of coins to solve this puzzle.
What is consensus?
Consensus means a general agreement among the members of a group or community. In centralized systems, the consensus is reached by the central institution itself. However, the whole community must reach a consensus in a decentralized system. In a blockchain, this mechanism is used to confirm transactions and produce new blocks to the chain. There are three consensus mechanisms.
is the oldest and most commonly used consensus mechanism. Miners create new blocks by solving a mathematical puzzle. The first miner to complete this task gets rewarded. There are advantages and disadvantages to this system. One advantage is that it is the most tested mechanism and, therefore, the least error-prone. However, mining has become more and more power-consuming. This makes it not only expensive but also harmful to the environment. The two most well-known cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin and Ethereum, utilize proof of work.
is a consensus algorithm where the validation of new blocks depends on a validator’s economic stake in the network. The blockchain keeps track of validators, and anyone who holds the blockchain’s base currency can become a validator. To become a validator, you must send a special transaction that locks up your “stake” in a deposit. The higher your stake is, the easier it is to create new blocks as a validator. The biggest advantage of this type of consensus algorithm is that it is not power-consuming like proof of work. Ethereum has announced that they are slowly switching their consensus algorithm from proof of work to proof of stake.
A fork is a change to the protocol of a blockchain. The changes in the protocol are so significant that the consensus is split into two parts. When the protocol of a cryptocurrency gets updated, a soft or hard fork has to be initiated so that the changes become effective.
A soft fork is an update of the existing protocol. The old version of the protocol will still be accepted, however it doesn’t feature the functions of the new protocol. This means that a soft fork is backward compatible.
A hard fork is like an upgrade of the blockchain. This upgrade is not backward compatible, meaning the old blockchain version will not be supported after a hard fork. Furthermore, the community is split into two sides after a hard fork. One side is with users of the old blockchain, and the other side is with users of the upgraded blockchain.